On the eve of the Beijing Olympics, one of the biggest unpaid sports events on the planet, a new report published today by the World Players Association shows that athletes and players continue to be denied a fair share of the wealth they generate and are excluded from the decision-making table.
The World Player’s report, the Economics of International Sport Governing Bodies, analyses the most up-to-date financial information from major sports bodies and compares it to the earnings of athletes.
The report shows that despite anticipated financial impacts from COVID-19, the multi-billion-dollar global sport industry remains resilient. Sacrifices made by players during the pandemic, including compliance with rigorous protocols and intensified playing demands, enabled the world’s major sports organisations to generate revenue putting them among the world’s leading businesses whilst holding hundreds of millions of dollars in reserve. For example, in 2020, the International Olympic Committee (IOC), still generated $621 million (USD) in revenue, despite postponing the Tokyo Olympics.
At the same time, research by World Players affiliates, including FIFPRO (here and here) and EU Athletes, demonstrates it is the players who have been the hardest hit by the crisis with many cases of contracts being terminated and cuts to essential services such as player development & wellbeing support at a time where this has been needed most.
The prioritisation of the commercial interests of major sports organisations above players is particularly evident when it comes to mega sporting events. Players have no say in where these tournaments are hosted and under what terms.
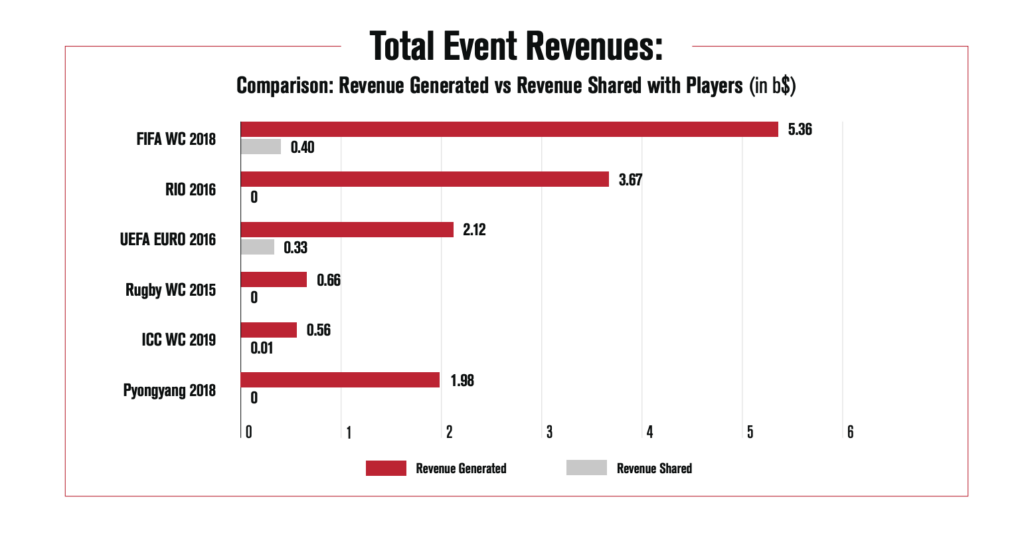
When it comes to the Olympics, the IOC, generated approximately $5.65 billion (USD) from the Rio and PyeongChang Olympics, yet actively limits athlete earning potential through ‘rule 40’ and various other means.
World Players Association Director of Legal & Player Relations, Matthew Graham, said:
“The Olympic Games is the economic engine of the IOC and is fuelled by a global unpaid workforce with the almost 3,000 athletes competing not directly sharing in any of the revenue they generate. Most of these athletes struggle to make ends meet and make incredible sacrifices for their sport and country yet receive incredibly limited support.”
The report also highlights even where some prize money is shared with players, such as in football and cricket, it forms a very low share of overall revenue with the inequity confronted by athletes exacerbated by worsening gender inequality.
To address these longstanding challenges, major global sport businesses must acknowledge that athletes are the labour and the product upon which the immense wealth of the industry is built and ensure respect for their economic rights. This includes undertaking economic rights due diligence and ensuring full respect for players’ rights to organise and bargain collectively. Collective bargaining has proved a win-win for many sophisticated parts of the global sports business, including major professional leagues, yet is actively resisted by the IOC and elements of the Olympic Movement.
The report finally identifies several trends that are likely to shape the future direction of the industry, including the rise and influence of private equity, exploitation of player data, and increasing proliferation of ways to monetise athlete name, image and likeness including through NFTs and other means. Whilst these may present enormous potential, lessons from the past must be learnt, including that the players are key to future-proofing the industry from economic and other challenges that lie ahead.
ENDS
The World Players Association, part of UNI Global Union, is the exclusive global voice of organized players and athletes across professional sport. It brings together 85,000 players through more than 100 player associations in over 60 countries. Its role is to ensure that the voice of organized players is heard at the highest levels in the decision-making of international sport..
For more information, please contact Léonie Guguen, Senior Communications Manager, UNI Global Union. Tel: +41 79 137 5436 or Email: leonie.guguen@uniglobalunion.org







