116 Groups Urge Prime Minister Suga to Take Action
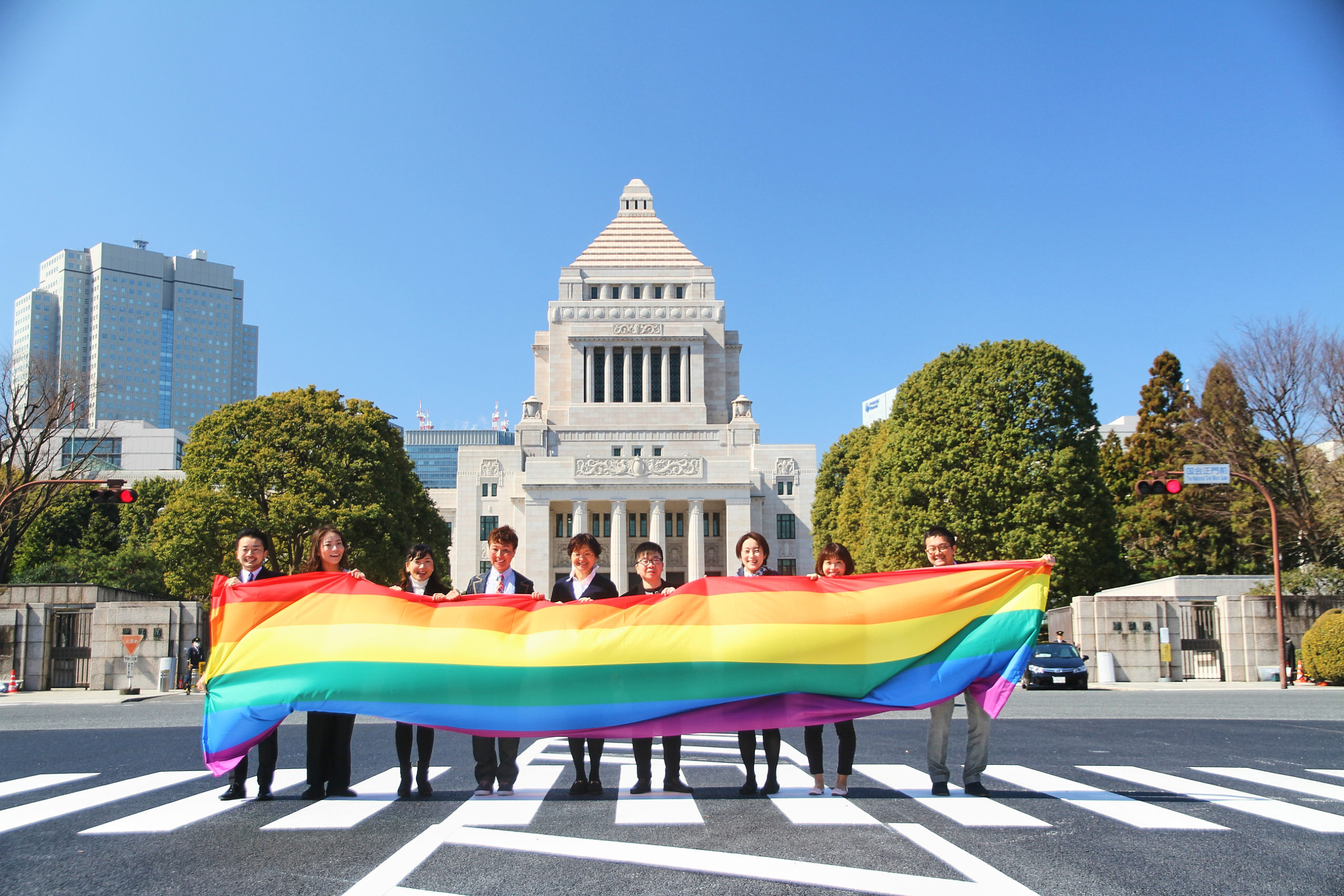
(Tokyo) – Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga of Japan should commit to introducing a law to protect against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity, J-ALL, Athlete Ally, All Out and Human Rights Watch said today. 116 human rights and lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) organizations sent a letter supporting such legislation to the prime minister on January 25, 2021, six months ahead of the day when the torch is scheduled to be lit at the Tokyo Olympics.
Tokyo was slated to host the 2020 Summer Olympics, but the International Olympic Committee and the Japanese government postponed the games for a year due to the Covid-19 pandemic. The Tokyo 2020 Summer Games are advertised as celebrating “unity in diversity” and “passing on a legacy for the future.” To do this, Japan needs to enact a national anti-discrimination law to protect LGBT people and athletes in a way that meets international standards. The groups are running an #EqualityActJapan campaign in Japanese and English in support of a law to prohibit discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity.
Take Action: #EqualityActJapan
We call on Japan’s government to introduce and enact legislation to protect LGBT people from discrimination before the Olympics. It’s time for an Equality Act – and the countdown starts now. TAKE ACTION
“LGBT people in Japan, including athletes, are entitled to equal protection under the law, but currently we have only one known openly out active athlete and many remain in the closet from fear and stigma,” said Yuri Igarashi, director of the Japan Alliance for LGBT Legislation (J-ALL), an umbrella organization of 80 LGBT organizations in Japan. “The Olympic Games give Japan a wonderful opportunity to introduce and pass protections so that everyone in society can live openly and safely.”
The Olympic Charter expressly bans “discrimination of any kind,” including on the grounds of sexual orientation as a “Fundamental Principle of Olympism.” Japan has also ratified core international human rights treaties that obligate the government to protect against discrimination, including the International Covenants on Civil and Political Rights and on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
“We have seen through history the power of the Olympics to mobilize athletes and fans to speak out for what they believe in, from Tommie Smith and John Carlos protesting racism in 1968 to the Principle 6 campaign fighting for LGBT athlete rights in 2014,” said Hudson Taylor, founder and executive director of Athlete Ally. “Sport teaches us that we are stronger when we stand together, and now is the time for the global sport community to stand in solidarity with the LGBT community in Japan.”
Japanese LGBT groups have pressed for six years to pass legislation to protect their rights, and their progress is seen in sharply changing attitudes in Japanese society, with public support for LGBT equality surging in recent years. In November, a nationwide public opinion survey found that 88 percent of those polled “agree or somewhat agree” with the “introduction of laws or ordinances that ban bullying and discrimination (in relation to sexual minorities).”
Japan’s national government has not enacted anti-discrimination legislation on the grounds of sexual orientation and gender identity. But in October 2018 the Tokyo metropolitan government adopted an ordinance that protects LGBT people from discrimination in line with the Olympic Charter. This municipal “Olympics” law was a direct result of a human rights consultation tied to the Olympics, and has proven popular. But it has also shown gaps in protection across the country and the need for a national approach, the groups said.
“This year, all eyes will be on Japan,” said Matt Beard, executive director at All Out. “In these trying times, the Olympic Games will be a welcome and much-needed celebration of humanity in all its beautiful diversity. By granting LGBT people protection from discrimination, Japan can prove that it truly supports the Olympic spirit of promoting tolerance and respect.”
Japan has increasingly taken a leadership role at the United Nations by voting for both the 2011 and 2014 Human Rights Council resolutions calling for an end to violence and discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. But LGBT people in Japan continue to face intense social pressure and fewer legal protections than other Japanese.
“By passing landmark legislation to protect LGBT people including athletes, Japan not only can be a global LGBT rights leader, but it would also become part of Japan’s permanent Olympic legacy,” said Kanae Doi, Japan director at Human Rights Watch.